According to GS1, a barcode is a machine-readable representation of data in patterns that can be electronically scanned using laser or image-based systems. Using specific symbologies, they encode identification information (product name, batch, location) and critical attributes (serial number, lot number, date).
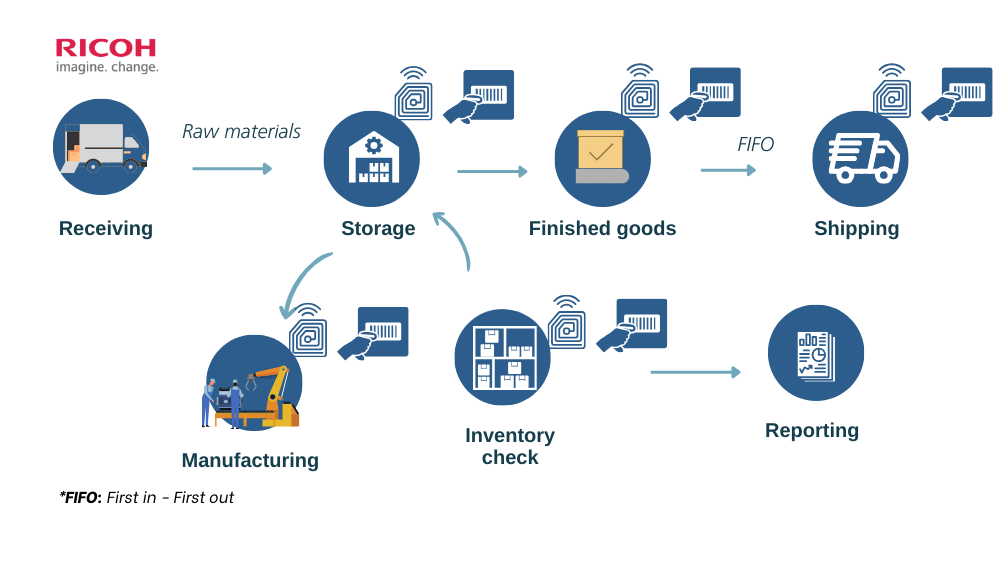
Barcodes are essential to the supply chain because they allow all parties involved-retailers, manufacturers, shipping companies, and hospitals-to automatically identify and monitor patients as they pass through the system.
- The barcode is created by encoding data into patterns of bars and spaces.
- When information needs to be retrieved, a barcode scanner reads and decodes the data from the barcode.
- The decoded information is then transmitted to a computer for processing, storage, or display.
It’s important to note that when using barcodes, the contrast between the light (white) and dark (black) components must be ensured, as during the scanning process, the scanner projects a beam of light onto the barcode and receives the reflected light for decoding.
Barcodes 1D
Barcodes1D (or linear barcodes) contain information horizontally and are the most commonly used type. This is the traditional and simplest form of barcodes. The black and white bars on 1D barcodes represent numbers and characters through encoding. 1D barcodes are frequently used to encode fundamental data, including product codes, prices, and other pertinent information.
Common types of 1D barcodes include:
- UPC (Universal Product Code): Widely used in retail worldwide
- EAN (European Article Numbering): Common in Europe and other countries globally
- Code 39: An alphanumeric barcode widely used in industry
- Code 128: A higher density barcode allowing the encoding of more characters and symbols
- Codabar: Commonly used in transportation and logistics

Barcodes 2D
2D barcodes (or matrix barcodes) contain information in both horizontal and vertical directions. This type of barcode has a higher data storage capacity than 1D barcodes and is increasingly used. 2D barcodes typically contain squares, dots, and other geometric patterns to encode information.
The following are the most typical kinds of 2D barcodes:
- QR Code (Quick Response): More information is stored in this most widely used 2D barcode than in 1D barcodes. QR codes are commonly used in advertising, mobile payments, and product tracking.
- Data Matrix: A 2D barcode in industrial applications featuring high data storage capacity and damage resistance.
- Aztec Code: A 2D barcode system designed to store data efficiently in a small space

The table below compares the key differences between 1D and 2D barcodes:
| Criteria | 1D Barcodes | 2D Barcodes |
| Principles | Use horizontal lines | Use horizontal & vertical lines |
| Volume | Less (~20 characters) | More (thousands of characters) |
| Encryption capability | Numbers and some specific characters only | Numbers, characters, images, and many other data formats |
| Error acceptance rate | Low, easily damaged when soiled or damaged | High, can withstand 30% damage, barcodes are still readable |
| Scan speed | Faster | Slower |
| Size | Smaller | Bigger |
| Application | Retail products, logistics, transportation | Logistics, Healthcare, industry, electronics, manufacturing, e-commerce, information technology |
| Types | UPC, EAN, Code 39, Code 128, Codabar | QR Code, Data Matrix, Aztec Code |
In summary, 2D barcodes offer several advantages over 1D barcodes, such as higher data storage capacity, better error correction, and the ability to encode various types of information. However, 1D barcodes are still widely used due to their fast scanning speed and compact size.
The choice between barcode types depends on the specific needs and applications of the business. Companies may consider using a combination of both 1D and 2D barcodes to suit different purposes.
Barcodes have widespread applications across various industries. Here are some instances of the various industries that use barcodes:
Manufacturing Industry
- Product and component tracking throughout production: Barcodes are attached to products and components for progress monitoring and origin traceability.
- Integration with production management systems: Synchronized with manufacturing software to improve production efficiency.
- Improved production efficiency and error reduction: Shortened processing times, improved lookup capabilities, increased productivity, and enhanced accuracy.
Electronics Industry
- Asset management and product lifecycle tracking: Barcodes manage and track the status and lifecycles of assets and equipment.
- Increased transparency and origin traceability: Decoded barcode information enables quick and clear identification and lookup.
- Prerequisite role in automated assembly processes from identification, location determination, and data recording.
Healthcare Industry
- Patient record and pharmaceutical management: Barcodes are attached to medical records, prescriptions, blood bags, etc., enabling tracking of patient information and drug status.
- Supply and distribution control of medical equipment: Barcodes are used to manage inventory and track the movement of medical equipment.
- Improved service quality and patient safety: Barcode implementation helps reduce errors, increase accuracy, and improve healthcare service quality.
Food Processing Industry
- Origin traceability and quality assurance: Product information can always be traced back via barcodes
- Monitoring transportation and reducing errors for businesses
- Easy access to nutritional information, recommendations, and origin for customers
Transportation and Logistics Industry
- Shipment management and tracking: Barcodes on labels and shipping documents enable shipment status and route tracking.
- Integration with supply chain management systems: Barcode information is shared among supply chain entities, increasing transparency and efficiency.
- Reduced errors and increased transparency: Minimizing issues like wrong delivery addresses and misplaced shipments while allowing customers to self-monitor delivery processes.
- Inventory management and product information: Managing stock levels, tracking product origin and location in warehouses
- Automated checkout: Accelerating the checkout process, reducing errors, or enabling self-checkout
- Integration with sales management systems: Barcode information is synchronized with sales management software for accurate sales data tracking.
- Initial investment costs: To implement a barcode system, users need to invest in barcode readers, barcode printers, labels, and management software. This cost can be a barrier for small businesses and individuals wanting to apply barcodes.
- Data security and privacy: Although barcode systems provide many benefits for businesses and consumers, processing and storing product data and customer information should be proactively prioritized.
- Implementation complexity: To install and configure barcode readers, create and print labels, and set up management software, barcode systems require technical expertise and abilities. For people who require assistance from professionals or expertise, this may be difficult.
- Barcode durability: Barcodes can fade or get erased over time. If barcodes become unreadable, retrieving information or identifying product origins will be difficult. This requires system synchronization during implementation to ensure label quality and suitability.
- Limitations in working environments: Barcodes may become damaged or illegible in places with high temperatures, humidity, dust, or other harsh circumstances.


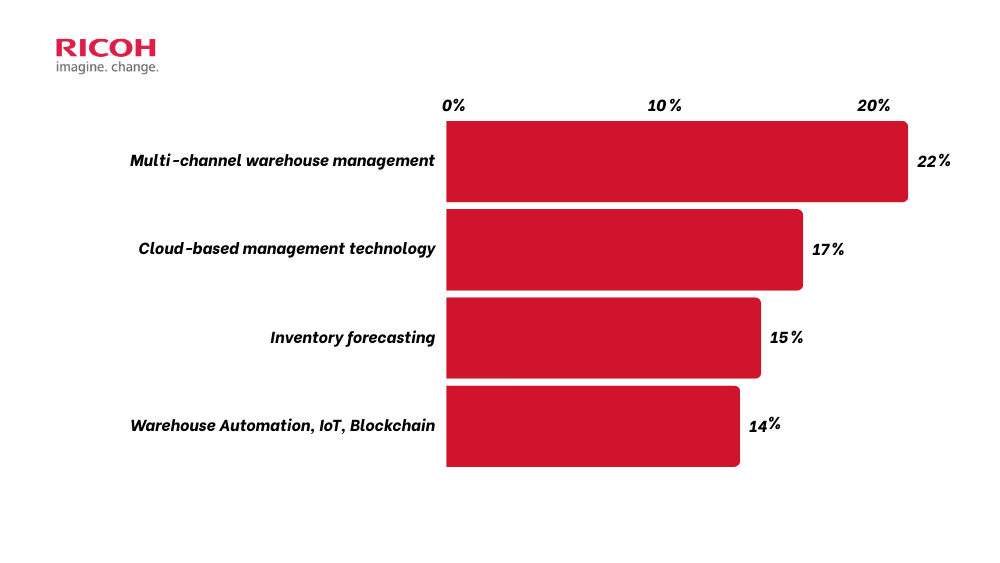 Warehouse management trends in 2024 from the perspective and research of Ricoh.
Warehouse management trends in 2024 from the perspective and research of Ricoh.